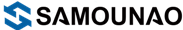Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
hobby or can be taken up as a serious career.
Lead Acid Battery
The term "MF" & “Maintenance Free”, which is applied to all VRLA batteries, has to do with the fact that no additional water is ever required.Periodic cleaning may be necessary and charging will most likely be required during extended periods of inactivity or if your vehicle has a significant amount of key-off drain.
VRLA MF batteries , which refer to Valve Regulated Lead Acid , Maintenance-Free. batteries ,are permanently sealed and never require the addition of distilled water.
Whether you own a motorcycle shop or are simply a parts enthusiast, understanding battery shelf life will help you ensure that you get the most out of your battery. In this guide, we’ll cover how battery power becomes depleted over time and even outline some simple tricks to extend the shelf life of your battery when it’s not in use.
What Does Battery Shelf Life Mean?
Battery shelf life can refer to the battery expiration date—which is the latest date that manufacturers can guarantee the best performance from the product. Many types of batteries can continue to function perfectly fine after the expiration date has passed. However, even though batteries have a long shelf life, they won’t maintain the same effectiveness if they’ve been sitting around for too long.
The charging power of a battery will become depleted over time, even if it’s not in use. Additionally, sealed lead acid batteries can also succumb to sulfation—which happens when the electrolyte begins to break down and stick to the lead plates to become sulfuric crystals.
Once sulfation occurs, salvaging the battery can be difficult or impossible, so it’s best to use batteries well within their recommended timespan.
What is a Self Discharge Rate?
Many people assume that batteries retain their full strength until used, but batteries do lose charge while sitting idle. The speed at which power is depleted while not in active use called “self discharge rate.” There are many factors that can impact self discharge rate, but one of the biggest variables is simply the battery brand. The higher quality battery, the slower the discharge rate.
How to Extend Battery Shelf Life
Although time is eventually the enemy of most batteries, there are a couple of tricks you can use to extend the shelf life of your batteries. The first (and simplest) method you can try is to store your batteries at a cool temperature. By storing your batteries at 50 degrees Fahrenheit or less, you can slow the aging process.
Another way to extend battery shelf life is to use a battery maintainer to keep the power level as consistent as possible. These products are specifically designed to maximize battery life and some can even prevent sulfation through a process of active desulfation.
So, How Long is the Shelf Life of a Battery?
If properly stored and maintained, most sealed lead acid batteries can sit on a shelf for about three years and should be expected to perform adequately for about another three years after they’re put into use. In order to ensure the best performance from your battery, pay attention to the date printed on the outside of the battery by the manufacturer.
Refer to How to properly store and maintain your battery.
The most important tool is a Powersports battery charger/maintainer. Only use a battery charger that is designed for Powersports batteries.Using a Fast-Charge or Automotive-charger can permanently damage your battery.
An inexpensive voltmeter or multi-meter is a smart investment if you have a number of vehicles with batteries to maintain.
If you own a Conventional battery, you should purchase distilled water to “top off” the cells when the electrolyte levels drop.
Wrenches and a screwdriver are required if you intend to remove the battery from your vehicle or tighten the terminal connections.
Baking soda, an old toothbrush, and wire brush to clean the battery and lead terminals.

A battery only requires a little monthly maintenance to perform perfectly. Keep the battery charged to 100%, recharging when the lights dim, the starter sounds weak, or the battery hasn’t been used in more than two weeks. Follow the simple battery storage check list below once a month:
STORING YOUR BATTERY
If the powersports vehicle is in storage or used infrequently, disconnect the battery cable to eliminate drain from electrical equipment.
Check the battery every month (for Conventional types) and every three months for AGM batteries.
For long storage or infrequent use, disconnect the battery cables from the vehicle to eliminate battery drain from electrical equipment.
Fully charge battery before storage using a Yuasa approved charger.
Regularly check battery as advised on battery maintenance page
If possible, remove battery from vehicle
--Clean the battery and terminals with a solution of baking soda and water to neutralize any electrolyte that may be on the outside of the battery.
--Be careful that nothing enters the battery during cleaning.
--The same solution can be used to clean the battery compartment to neutralize any electrolyte that may be present.
--Rinse with clean water and dry thoroughly.
--After the battery is cleaned, inspect carefully for any signs of damage or extraordinary wear that may have occurred during use. If you have any concerns, you should seek the advice of a mechanic or a battery specialist.
When removing your vehicle from storage for use, follow the same steps above and the steps on the battery maintenance page to check the battery’s condition.
Even with proper maintenance, batteries will not last forever and will need to eventually be replaced.
Any device that stores energy can be dangerous. There is a lot of explosive power in a gallon of gasoline, but when handled with some knowledge its use can be made relatively safe. Batteries are no different in that with the proper precautions and safety practices, they can be handled in a safe manner. Working with batteries poses two hazards: potentially explosive gases that are given off during discharging and charging, and sulfuric acid, which is highly corrosive. The following safety list below will help keep these two hazards under control:
No Smoking
--No smoking, sparks (from static electricity or other sources) or open flames around or near batteries
--Batteries can produce hydrogen gas that is highly flammable when combined with oxygen; if these gases ignite the battery case can rupture or explode
Eye Protection
-Always wear eye protection, protective gloves and protective clothing when handling a battery
Loosen Vent Caps
-On Conventional batteries, loosen vent caps when charging and ventilate the entire charging area
-A build-up of hydrogen and oxygen levels within the battery, or in the area where its being charged, can create a fire hazard
Overheating when Charging Battery
-If a battery feels hot to the touch during charging, stop charging and allow it to cool before resuming
-Excessive heat damages the plates, and a battery case that’s too hot during charging can rupture
Remove Red Sealing Cap
-On Conventional batteries, remove the red sealing cap from the vent elbow
-Never put the red sealing cap back on the battery once it is removed
-If sealing cap is left on, gas trapped inside the battery can explode
-For the same reason, make sure the vent tube isn’t kinked or blocked
Connecting Battery Charger Leads Properly
-Properly connect battery charger leads to the battery: positive to positive, negative to negative
-Unplug the charger, or turn it off before connecting or disconnecting the leads
-Minimizes the chances of creating sparks when connecting or removing the leads from the battery
Acid Spills
-Clean up acid spills immediately, using a water and baking soda solution to neutralize battery acid (1 lb. baking soda in 1 gal. water)
Acid
-Make sure battery acid fill containers are clearly marked and work areas are well lighted
-If sulfuric acid is swallowed or splashed in the eyes, take immediate action
-Sulfuric acid in the eyes can cause blindness
-Diluted sulfuric acid used as electrolyte can burn the skin
-Ingesting or swallowing sulfuric acid can cause serious internal injuries or death
The longer you can keep your motorcycle battery functioning properly, the less frequently you’ll need to replace it. Not to mention the
frustration that can come along with diagnosing the issue of a dead battery, the time it takes to research the type of battery you need, and the expense of frequent replacements. Luckily, there are a few tricks you can use to extend the life of your motorcycle battery, so you can spend less time worrying about your battery life and more time on the road.
Keep it Charged
The absolute best thing you can do to keep your motorcycle battery working stronger for longer is to make sure it stays charged. If you ride your motorcycle daily, the alternator should take care of charging the battery while you ride, but if you keep your bike in storage for weeks or months at a time, you’ll need to invest in a motorcycle battery charger.
Stick to a Maintenance Schedule
As with most components of your motorcycle, the battery needs maintenance too. Some routine maintenance you can easily implement includes:
Check terminals for signs of corrosion and clean off any deterioration with a wire brush.
For conventional batteries, check the electrolyte levels and add distilled water if the plates are not submerged.
Test your battery’s power with a battery tester to make sure it’s functioning properly.
All of these simple checks and adjustments should be done on a monthly basis and can go a long way toward extending the life of your battery.
Regulate the Temperature
Vapor loss is a normal occurrence for conventional motorcycle batteries that happens gradually over time. However, extreme shifts in temperature can expedite vapor loss, which will eventually cause the battery to stop holding its charge. Even though there’s no way to protect your motorcycle from all temperature fluctuations, storing it in a climate-controlled garage will keep your battery at a stable temperature while not in use.
For YTX, YIX, and GYZ series batteries, vapor loss is not an issue because they are sealed and the gases recombine inside the battery so that no fluid is lost from the battery. However, storing them in a climate-controlled garage will reduce self-discharge and keep the batteries at a stable temperature for reliable starting all year long.
Use the Proper Battery for Your Motorcycle
Not all bikes are created equal. The same goes for batteries. By making sure you’re using a battery that is designed to be used with your specific model of motorcycle, the better it’ll perform. We know it can be tough to know which battery is best suited for your bike, which is exactly why we created our battery finder to ensure that you know which to choose.
It’s also important to note that when it comes to motorcycle batteries, brand matters. my brand is the most trusted brand of motorcycle battery on the market—and has been for decades. That’s because we’ve taken all the maintenance factors into account and designed our high-performance products to combat all the usual causes of wear.
The engineering behind our products has led to improved low-temperature performance and many of our products do not require the typical maintenance you’d need with other battery brands. For instance, most of our products are designed to be airtight and spill-proof—which means they don’t require water to be added. Additionally, the corrosion-resistant nature of our products combats against rust and deterioration. All of these considerations make it one of the most maintenance-free batteries available.
If you’re searching for a motorcycle battery that offers the longest life with the least amount of maintenance, my brand is the best choice. All of our products are designed with real-life use in mind. When we say, “We respect the ride,” we mean that our batteries won’t stand between you and the experience of the open road. You can count on your battery to start the first time, every time.
If your bike has been sitting in storage for a long period of time, you’ll need to run through your battery maintenance checklist before hitting the road. One important element of a battery’s function is the condition of the terminals. By learning how to clean corroded battery terminals, you can keep your battery functioning properly and extend its lifespan.
What Causes Battery Corrosion?
The most common cause of battery corrosion is when hydrogen gas released from battery acid causes a chemical reaction with the metal terminals. Corrosion typically looks like a flaky layer of white or green discoloration that sits on your battery terminals.
It’s important to note the color of the buildup that’s collected on your terminals because different colors can indicate the difference between corrosion and sulfation.
What’s the Difference Between Corrosion and Sulfation?
Although these two processes produce relatively similar-looking discharge, there are a few key differences between corrosion and sulfation.
-Corrosion Occurs when hydrogen gas released from the battery acid reacts with the metal terminals. It is white or blue/green in color.
-Sulfation Test your battery’s power with a battery tester to make sure it’s functioning properly.
It is important to identify the difference between these two chemical reactions because corrosion can be easily removed as part of a regular maintenance routine, while sulfation typically indicates deeper damage to the battery. When a battery reaches the sulfation stage, the best thing to do is to replace the battery.
Steps for Cleaning Corroded Battery Terminals
Cleaning corroded battery terminals is easier than it sounds. Follow these easy steps to get your battery back into peak condition:
--Make sure your motorcycle is turned off, then you can remove the battery.
--Avoid touching with your bare hands and use a wire brush to remove the majority of the corroded material.
--Using a rag, apply a mixture of water and baking soda. This acts as a base to neutralize the acid.
--Scrub the baking soda mixture into the terminals using your wire brush. You can also use a toothbrush if you want to get more detailed.
--Wipe off any excess solution from the terminals with a rag or paper towel.
--Let your battery dry completely before reconnecting the terminals to your motorcycle.
Overall, removing corrosion from your battery is an easy way to get the most out of your battery. Complete this process after long periods of storage to ensure a complete connection between the battery and the machine
What is an AGM Battery?
We talk a lot about AGM batteries. But what does AGM actually mean? In this quick guide, we will cover some of the basics about AGM batteries, including what sets them apart from conventional style batteries and some of the advantages of choosing an AGM battery for your vehicle. AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat and is an advanced type of lead acid battery that is sealed, spill-free, and maintenance-free.
What is the Difference Between Conventional and AGM Batteries?
Conventional batteries are sometimes called “flooded” because they contain electrolyte that moves freely inside the battery encasement. This design used to be the standard style of lead acid battery, but has since lost popularity in favor of sealed AGM batteries.
While conventional batteries are still the most cost-effective style of lead acid batteries, they often have a shorter lifespan and require regular maintenance.
What are the Advantages of AGM Batteries?
AGM batteries hold their charge well and are less likely to sulfate when compared to regular wet cell batteries (conventional battery types). Because of this, they are a great choice for vehicles that are not used daily. Because the liquid electrolyte flows freely inside conventional batteries, they must be mounted and stored upright to prevent leakage. AGM batteries, on the other hand, can be mounted in any orientation because the liquid is sealed inside the battery. Another advantage of the electrolyte being suspended inside the battery is that it is more resistant to vibration, which is especially important for ATVs or other vehicles that operate on uneven surfaces.
Whether you’re hoping to replace your existing battery or are purchasing a new battery for the first time, it’s important to understand the difference between AGM and conventional batteries. If you use your vehicle every day and are looking for a cost-effective option, a conventional battery may be right for you. However, if you need a battery for your ATV, snowmobile, or other powersports vehicle that you ride only seasonally, an AGM battery is likely the best option.
Always keep the acid level between lower and upper lines on front side of the container (conventional type batteries)
Do not let the battery stand in a discharged condition.
Charge battery once a month
When your motorcycle is stored over 30 days, plug in a Yuasa automatic battery charger to maintain a proper storage charge
Keep battery top clean, dry and free of dirt
Clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion. Inspect vent tube, ensuring that it is not bent, twisted or clogged.
Protect the battery from strong impacts or shocks
For additional battery maintenance and storage information.
When a battery is in an excessively discharged state, it does not readily accept a standard charge. The battery may appear to be accepting a charge, but charging is occurring only at the surface of the plates.
With an AGM (sealed lead-acid) battery, higher voltage is required to get the job done. Charge the battery using a charger that can consistently supply between 18 and 20 volts. Typically a charger like this is only found in the service department of a motorcycle shop. The service technician should test the battery prior to charging, and again after charging is complete. Charge time will vary based on how bad the battery is discharged. Final testing will tell you if the battery has been recovered, and to what extent.
With a conventional (flooded) lead-acid battery, slightly higher than normal charging amps are required to recover the battery from an excessively discharged state. This higher rate could be up to 10 amps, but no more. The battery may get warm during charging, but this is a good sign. It means the battery is charging. Make sure the battery’s water level is up to the top line before charging, and monitor throughout the charging process to make sure no additional water is lost. If so, replace water as needed.
If the battery still does not hold a charge after going through these procedures, best bet is to purchase a new battery. In order to ensure that the new battery does not suffer the same fate, make sure battery is charged properly and frequently enough to keep it from draining to an excessively discharged state. Charging once a month is recommended in most cases. More frequent charging may be required on today’s vehicles that tend to have a constant electrical drain. Typically, electrical drain can come from a radio, clock, alarm system, or other computer memory.
VRLA: Valve Regulated Lead Acid
MF: Maintenance-Free
AGM: Absorbed Glass Mat
SLA: Sealed Lead Acid.
The maintenance on a VRLA battery is much easier than the Conventional types. There is no need to check electrolyte levels and the filler plugs should never be removed. *The term “Maintenance-Free”, which is applied to all VRLA batteries, has to do with the fact that no addiional water is ever required.
Keep the battery and terminal posts clean. If required, follow the cleaning procedures outlined in the How to Maintain Conventional Batteries section.
Check the battery voltage and charge if necessary. Full charge voltage for a VRLA Maintenance-Free battery is 12.8V to 13.0V. When charging the battery, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions provided with the charger.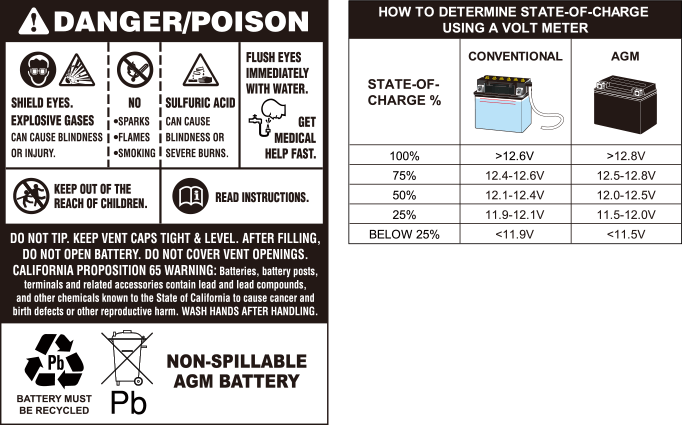
** CAUTION! Before performing any maintenance to your battery, make sure you have the adequate personal protection gear. It’s necessary to shield your eyes, skin, and clothing. Also, never smoke near a battery or expose it to an open flame or sparks. Read the owner’s manual and follow the instructions and all warnings included with the battery.
The electrolyte levels must be maintained above the “Lower Level” indicator lines and not above the “Upper Level” lines. Allowing the electrolyte levels to fall too low will damage the battery plates and overfilling the battery could result in leakage.
If the electrolyte levels are below the “Lower Level” indicator lines, add distilled water. Never “top off” a battery with electrolyte, only use distilled water!
Make sure that the flexible exhaust tube is securely attached to the battery exhaust port and is not clogged or pinched.
If the battery is dirty, clean it with a solution of baking soda and water applied with an old toothbrush. Dirt and grime can create a conductive path that will discharge the battery. Rinse with clean water and wipe dry with a paper towel.
Clean the battery terminals and battery harness with a small wire brush or emery cloth. Replace the battery if the terminals are cracked.
Check the battery voltage and charge if necessary. Full charge voltage for a conventional battery is 12.6V to 12.8V. When charging the battery, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions provided with the charger.
** CAUTION! Before performing any maintenance to your battery, make sure you have the adequate personal protection gear. It’s necessary to shield your eyes, skin, and clothing. Also, never smoke near a battery or expose it to an open flame or sparks. Read the owner’s manual and follow the instructions and all warnings included with the battery.
Many factors affect the life of a battery:
Climate: Colder climates tend to be hard on batteries from a starting standpoint, and for the fact that many people put their bikes away for the season when not using. Sometimes without charging properly. Hotter climates tend to discharge batteries quicker, and dry out batteries quicker. “Average” climates are the best for long battery life.
Usage: A battery that is used every day has the most chance of living a long life. Batteries that sit a lot, many times are neglected. This shortens overall life. Periodic charging is the best defense.
Application: How well is the battery charged in the vehicle? Some vehicles have better charging systems than others. Older bikes have worse charging systems than new ones. Are there a lot of extra accessories on your vehicle? Sometimes a battery has a hard time keeping up with additional electrical drains, thus wearing it out quicker.
Negative Factors:
Sulfation: A build up of crystals on the plates of a battery. This comes from not charging a battery properly. The more sulfation that builds up, the harder the battery is to charge, until finally it does not charge at all.
Water Loss: Can come from overcharging, or just simple evaporation over time. This only happens with conventional batteries. This does not happen with sealed AGM batteries. Once the plates of a battery are left open to the air, above the fluid level, they can corrode very quickly. Corrosion can cause an internal short, and very quickly destroy the battery. Keeping proper water levels maintained is very important.
Lack of Charging: As mentioned previously, lack of proper charging is the main reason that a battery will not last as long as it should. At the very minimum, a battery should be charged once a month if left unused.
Complete Drain: Have you ever left your key on, and totally killed the battery? If recovered in a short time period, the battery should charge back to 100%. But every time this happens, it is similar to the battery having a “heart attack”, and shortening its overall life. Always turn your vehicle off with the keyed ignition switch, not the “kill switch”.
Better Battery Choice:
AGM: Sealed AGM batteries typically last 2 to 4 years on average. 5 to 6 years is easily obtainable with proper maintenance. Typically sealed AGM batteries will give warning before completely dying. They will start slower, and require more charging. This is your clue to replace the battery. Typically they do not fail all of a sudden.
Conventional: Conventional “acid-filled” batteries have a harder life, for many of the reasons listed above. Conventional batteries typically only last 1 to 2 years on average. Although, 3 to 4 years is possible, in the best environments, and with excellent maintenance.
The following characteristics will tell you if a battery has been properly charged:
The specific gravity of the acid is over 1.275 (conventional type batteries only)
Maximum voltage output across battery terminals can be maintained at constant level for two hours
Open circuit voltage is stabilized at 12.7 volt or higher at 6.3 volt or higher for 6 volt batteries
If you intend to store your Powersports vehicle for the offseason or don’t plan on using it for an extended period of time, always make sure that the battery is maintained at or near a full state of charge.
When storing your vehicle for more than two weeks, it is recommended to remove the battery from the vehicle and store it in a cool, dry place.
Check the battery voltage every two weeks, if you store it in temperatures above 60°F and monthly if you store it below 60°F. Charge your battery if the voltage falls below 12.60V for a Conventional type and 12.80V for a VRLA Maintenance-Free type. While Powersports batteries can be stored safely at a wide range of temperatures, lower temperatures are preferred as this reduces the amount of self-discharge. If a battery is deeply discharged and stored in temperatures below 32°F, the electrolyte could freeze and permanently damage the battery. If the battery is maintained at a full state of charge, there is little chance of freezing even in sub-zero temperatures.

What Are Cold Cranking Amps?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is an industry value to rate a batteries’ ability to start a powersports engine in cold temperatures. The numerical value refers to the number of amps (current) a 12-volt battery can produce and sustain for 30 seconds at a temperature of 0 degrees Fahrenheit while maintaining at least 7.2 volts.
Depending on the climate in which you live, the Cold Cranking Amps are a crucial factor in selecting the ideal Yuasa battery for your motorcycle, UTV, ATV, PWC, or other powersports vehicle. View our comprehensive line of powersports batteries to find the right fit for your vehicle.
The relationship between your motorcycle battery and engine functions much in the same way as a car battery. The alternator is fitted with a regulator that charges the battery while you ride. However, it’s important to note that normal riding may not be enough to fully charge the battery after being completely depleted. For example, if you accidentally leave your headlight on overnight and find that the battery has died in the morning, the alternator in your bike may not provide enough power to fully replenish the charge after you jump start the engine. In this case, you may need to connect your battery to an external charger/maintainer.
Do Different Types of Bikes Provide Different Charging Power?
Whether your alternator can revive your dead battery largely depends on the type of motorcycle you own. Magnetic stators don’t charge at low RPMs. Your owner’s manual will tell you if a certain voltage is required in order for your alternator to begin charging your battery.
How Can I Tell if My Motorcycle Battery is Beyond Repair?
The only way to know the state of your battery for certain is to use a battery tester. This accessory determines the health of your battery in a matter of seconds, so you can find out if a good charging session will do the trick, or if it’s time to purchase a replacement battery.
Will My Alternator Charge the Battery if My Motorcycle is Running Stationary?
If you find that your motorcycle alternator is capable of recharging your dead battery, you will likely need to run the bike on the road in order for the alternator to work most effectively. It is recommended that you return to your garage after your ride in case the bike refuses to start up again after being shut off. In most cases, a ride on the road is enough of a recharge for normal use. However, if the battery is deeply depleted or dead, it may not start up again after being shut off. If this happens, we recommend using a charger/maintainer to bring the battery up to a fully charged state.
Regardless of what type of motorcycle you own, every bike will have some type of alternator designed to keep your battery operating correctly while you ride. This is an important safety feature that riders rely on. But if you find that your bike has continuous issues starting up or your tester says your battery is dead—it’s time for a replacement. Remember that my batteries are the highest performing powersports batteries available. When it comes to replacing your battery, make sure you use my brand.
It is important to note, that even if you get your battery up and running again, a battery that has been too deeply depleted may continue to have issues for future starts.
You can use a digital print tester to determine the health of your battery and figure out if it needs to be replaced or simply needs a good recharge. Even though your alternator will charge the battery while the bike is running, you should test the charge status as soon as you get back to your garage in order to prevent future startup problems.
Rule Out Other Issues Before Jump Starting
There are plenty of factors that could prevent your motorcycle from starting—from carbon buildup on your spark plugs to something as simple as an empty gas tank. Make sure you go through your checklist of potential problems prior to attempting a jump start.
Some commonly overlooked start prevention culprits include:
Kickstand Safety Mechanism– Some bikes are built with a safety feature that prevents them from starting if the kickstand is down.
Gear Shift Safety Mechanism– In order to prevent the bike from accidentally starting while in gear, many models must be in neutral with the clutch engaged prior to starting.
Kill Switch– Kill switches are important safety components that make it easy to shut off the bike without having to fumble with the ignition keys. Make sure it’s not the reason your bike won’t start
Once you’ve determined for certain that the battery is the reason for your troubles, it’s time for a jump start.
How to Jump Start a Motorcycle Battery
Motorcycle batteries can be jump started from another motorcycle, car battery, or portable battery jump starter. Most motorists keep jumper cables in their car, so it shouldn’t be too hard to find someone who is willing to help you out. Once you have your live battery lined up,
follow these simple steps:
Connect the red positive terminal on the dead battery to the positive terminal on the live battery.
Clamp the black negative terminal on the live battery, but make sure you place the opposite negative clamp on a grounded and unpainted metal surface of your motorcycle. Typically, the chassis is suitable for this.
Start the motorcycle with the good battery. Do NOT start the car.
Allow it to run for a few minutes and then carefully disconnect the cables in the reverse order they were connected.
It’s important to place the negative clamp a safe distance from the battery because this connection often makes a spark and could cause a potential hazard. If your battery is a sealed Samounao AGM battery, there’s almost no risk of fire, but keeping the negative clamp away from the battery is a best practice.
Another important safety note is to make sure that the two cable ends do not touch each other. Touching the cable ends will certainly cause a spark—and if that spark reaches the hydrogen gas that is often emitted from certain types of batteries while they charge, it could cause
a serious fire or even explosion. So, even though jumping a battery is a relatively simple procedure, it’s so important to always use caution and take the process seriously.
Batteries are not eternal. Even the best quality battery has a maximum life expectancy. That’s because batteries are essentially boxes of chemicals and chemicals lose potency over time.
Difference Between a Dead Battery and a Bad Battery
Almost everyone has left their headlights on all night at some point. This slow draw of energy without the ability to recharge from the alternator is sure to drain the battery and cause it to “die.” In most cases, dead batteries can be revived by a jump start. The same is not true for a “bad” battery.
When a battery goes bad, there is no way to revive it. No matter how much you charge it, a bad battery won’t hold a charge.
Rule Out Other Potential Causes
The first step in any mechanical diagnosis is to rule out all the potential causes of the problem. If your battery is less than three years old, has never gone uncharged for a long period of time, and doesn’t show any visual signs of damage, there may be other reasons your bike won’t start.
Before you invest in a new battery, inspect the wiring, check if terminal connections are loose or corroded—you may even want to have your motorcycle professionally inspected to make sure it’s not an issue with your alternator or another mechanical component. Remember that many modern motorcycles are outfitted with a safety feature that prevents the bike from starting if the transmission is in gear and the clutch is not engaged, so always make sure you have the proper conditions to start your bike.
Visual Inspection
The most obvious warning signs can be found through a simple visual inspection. Signs of a bad battery include broken terminals, a crack or bulge in the plastic casing, as well as any leaking fluid or discoloration.
Sometimes, battery terminals can become corroded. In most cases, it’s possible to clean corroded battery terminals and continue using your battery, so make sure any signs of wear or discoloration are not a result of normal corrosion before you deem your battery “bad.”
Battery Testing
The surefire way to determine the health of your battery is to use a battery tester. A professional quality tester will be designed specifically for powersports batteries and provide recommended actions.
If your battery is indeed bad, the only solution is to replace it. Don’t choose just any replacement battery. Any time you need to purchase a replacement part for your motorcycle, it’s best to select a reputable brand so you don’t face the same issue again for a very long time. my Batteries are the number one choice of motorcycle manufacturers worldwide because the quality and longevity of my batteries far exceed that of its competitors. The next time you need to replace your motorcycle battery, choose my brand.
The life of a battery will last a long time with the correct care and maintenance. However, the charging power of any battery will become exhausted over time and replacement will be needed. It’s important to know how to dispose of a battery responsibly and to understand the impact it has on the environment.
What types of batteries can I recycle?
All AGM lead-acid batteries can be reclaimed and recycled into new products. This includes batteries found in all types of powersports vehicles, motorcycles, and automobiles.
How does battery recycling work?
The battery recycling process is quite simple. Expired batteries are broken down in a hammer mill and the various pieces are separated in a vat. The heavy materials like lead fall to the bottom while the lighter pieces like plastic rise to the top. After the pieces have been separated, they each go through their own unique recycling process.
The polypropylene plastic pieces are reclaimed and are made back into battery cases. The lead is melted and recast into parts for use in new batteries. The sulfuric acid in the battery is recycled in two different ways. One way is converting it into sodium sulfate, which is then used in detergents, textile, and glass manufacturing. Sulfuric acid can also be neutralized into water and released into the public sewer system.
Benefits of recycling batteries
The good news is that 99% of the materials that make up a lead acid battery can be recycled. This means that batteries are in a closed-loop cycle where recycled batteries go on to become new batteries. Batteries are unique in that they are some of the most recycled objects on the planet—even more so than aluminum cans or glass bottles! This is friendly to the environment because it keeps pollution and lead out of landfills while keeping costs down.
What to do with old batteries
Do not dispose of your used AGM lead-acid battery in the trash. Instead, you can return your old battery at many recycling locations including service shops, auto parts retailers, dealerships, and home improvement stores. The old battery will be collected, packed, and shipped to a recycling center where it will be handled in a safe manner.
For more information on where to drop-off spent batteries, refer to this database from Call2Recycle.
Improper handling of spent lead-acid batteries can have adverse effects on humans, animals, and the environment. Batteries contain highly toxic materials that can contaminate groundwater and cause serious harm if disposed of in a landfill.
Proper battery disposal procedures ensure safe and responsible recycling. It is better on the environment and the manufacturing process, which keeps new batteries at reasonable prices.
If a new battery becomes unserviceable within a few days or weeks after its installation it may be due to one or more of the following reasons:
A faulty charging system
A short circuit in the electrical system
Battery terminals are dirty or not properly connected
Excessive ignition off drains or high parasitic drains
Electrical capacity of the battery is insufficient for size of the vehicle
The battery has been inadequately activated, dissipating its strength from the outset
The battery, after being filled with acid has been left too long without initial charging, and has been allowed to become sulfated
Contact a qualified technician if condition remains the same.
In most applications, batteries are installed in an upright position, but in some situations there is a need to tilt them (sometimes at very extreme angles) or lay them completely flat on their backs.
Conventional “wet” style batteries should never be mounted in any orientation other than upright since there is liquid electrolyte that could escape the battery.
Maintenance-free, absorbed glass mat (AGM) style batteries offer more flexibility regarding mounting angles because the electrolyte is absorbed, not flowing freely.
Different battery models have different limitations regarding mounting angles.
For questions pertaining to specific batteries or specific vehicle applications, please contact with us
Lead Acid Battery Regeneration
This lead sulfate increases internal resistance and decreases the specific gravity of the electrolyte. The process of battery sulfation build-up is unavoidable. Worse yet, after 3-4 years the process accelerates substantially.
The battery was inactive for too long.
The battery was discharged too deeply.
The wrong charger was used.
A bad battery cell was left untreated.
The battery has reached too high/low temperatures.
The charge cycles were disrespected.
1st, using a special additives or adding activator,
the additives of Cobalt, Manganese and other substances. which was commonly used during the 2nd world war on submarine batteries. The result is a release of the superficial sulfate build-up. The acid level is elevated to normal and the battery capacity somewhat increases. this effect occurs depending on the degree of sulfation and age of the battery after a short period of time. in addition, a contaminant remains in the electrolyte. structural damage to the surface is not fixed and could even increase. furthermore, the hard sulfate crystals do not dissolve completely, and they can cause further contamination and degradation of the battery. In the long term, Silver and/or Cobalt compounds cause irreversible damage to the battery.
2nd , Large Current charge or Negative Pulse charge
large current with high energy to removal & activate lead acid crystal , remove sulfuration Adding negative pulse when charge , which can reducing the temperature rise. has a limited effect on 'Sulfuration Removal'‘, both of them would damage positive plate ,shorten battery life
3rd ,CompositResonant Pulse, which is BEST Opinon and Tech
Using variety harmonic pulse with special amplitude to resonate with coarse lead acid sulfate crystal , to absorb battery ‘sulfuration’,Almost no damage to battery.

For batteries that are between 1-2 years old, as sulfation occurs from the moment a battery is made. Batteries that have gone through the regeneration process hold and deliver their capacity constant at a 90-100% level,
Over a period of 8-10 years old battery may be regeneated till 80% capacity or more
AGM, GEL, VRLA, MF, Flooded, Dry, Traction, Deep cycle and Stationary battery etc , variety between 2V-72V (2~3000Ah) cells.
Sulfation of lead-acid batteries is the main reason for capacity loss and battery malfunctioning. With our SAMOUNAO battery reconditioning technology, you can now offer a second life to your batteries.
Battery reconditioning is very popular. 80% of the batteries breaking down and losing capacity are sulfated, but can be restored with the right equipment.
Our SAMOUNAO battery regenerator successfully removes sulphation due to an Composit Resonance Pulse process. which is a leading patent tech in the world , and without any damage on battery itself.
This process restores the battery capacity, giving you the ability to reuse old and sulfated batteries. You can also use the battery reconditioner for annual maintenance to strongly prolong the lifespan of your batteries.
Theory & Knowledge
Based on solid physics theory . any insulating layer can be breakdown if giving a enough high voltage , Once breakdown, insulating materials would be transformed into a conductor.
The same way ,large volume size lead sulfate crystals can be breakdown if giving a instant high voltage to Sulfation Layer with low conductivity & high resistance
Based on atomic physics, the sulfur ion has 5 different energy levels, meta-stable ions is tend to move to stable covalent energy levels.
In state of stable covalent bond energy level , sulfur molecular be existed in annular form that contains 8 atoms , which is a stable combination . it is very difficult to be broken and transition.
'Sulfuration' phenomenon on battery is refer to this kind of stable covalent energy levels . to break it , need to offer a certain energy to molecular with ring structure . electrons in the outer shell of sulfur atom is activated to the next high-energy band, stable covalent energy levels is broken and sulfur atoms are released
A cold battery may look charged actually be undercharged.
Check each cell... If the lowest cell is .050 points lower than the highest cell the battery is defective.
If water has just been added to the battery it will give a false hydrometer reading.
1st, using a special additives or adding activator,
the additives of Cobalt, Manganese and other substances. which was commonly used during the 2nd world war on submarine batteries. The result is a release of the superficial sulfate build-up. The acid level is elevated to normal and the battery capacity somewhat increases. this effect occurs depending on the degree of sulfation and age of the battery after a short period of time. in addition, a contaminant remains in the electrolyte. structural damage to the surface is not fixed and could even increase. furthermore, the hard sulfate crystals do not dissolve completely, and they can cause further contamination and degradation of the battery. In the long term, Silver and/or Cobalt compounds cause irreversible damage to the battery.
2nd , Large Current charge or Negative Pulse charge
large current with high energy to removal & activate lead acid crystal , remove sulfuration Adding negative pulse when charge , which can reducing the temperature rise. has a limited effect on 'Sulfuration Removal'‘, both of them would damage positive plate ,shorten battery life
3rd ,CompositResonant Pulse, which is BEST Opinon and Tech
Using variety harmonic pulse with special amplitude to resonate with coarse lead acid sulfate crystal , to absorb battery ‘sulfuration’,Almost no damage to battery.
They are very harmful to the environment.
It is illegal to place them in the trash or landfill.
Any business that sells batteries... is legally obligated to recycle them
Undercharge--Sulphation & Corrosion
Discharged Sotrage--Sulphation ,Corrosion & Hydration
Overdischarge--POS(+) Plate damage
Abuse-- Droped/Cracked --Boken posts --High heat --Poor Quality
Poor Maintenance-- lack of systematic power supply maintenance --lack testing
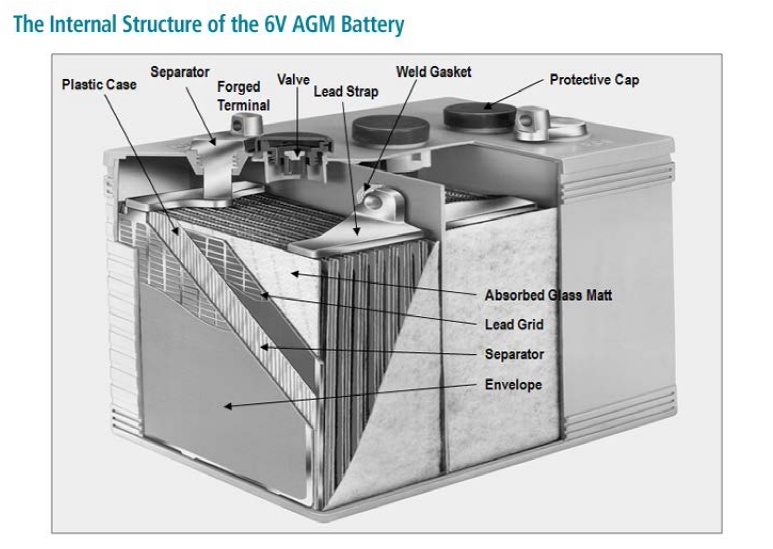
When the two dissimilar metal plates are immersed in acid they create a voltage.
This voltage is created by the concentrating Negative Ions on the negative plates and Positive Ions on the positive plates.
As batteries discharge the acid is turned to water and the lead plates are turned into lead sulfate.
When both plates are turned to lead sulfate the battery is discharged or dead.
Each cell is with 2.13 V; 2.13V*6=12.78V
Full Charger=12.78V or more
Discharge Battery =1.75V each cell
1.75V*6cells =10.5V (low voltage); <12V=discharge
Deep Cycle Battery: Designed to be regularly deeply discharged using mostly of its capcaity , Forklift ,Golf Cart, Lift etc
VRLA Battery(SLA Battery): Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery (Sealed Lead Acid Battery), Commonly known as a sealed battery or maintenance free battery,there is two primary type of VRLA battery, GEL type & AGM type
--GEL type :Gel cells add silicon dust to electrolyte ,forming a thick putty-like Gel
--AGM type:Absorbed Glass Matt force fibeglass mess between the battery plate with same basic outcome